Ejemplo 3
Antes de empezar
ToDo... Hablar un poco sobre estas...
Las siguientes figuras muestran casos de uso de encoders rotativos:
-
Acceso al menu de control de dispositivos como impresoras 3d:
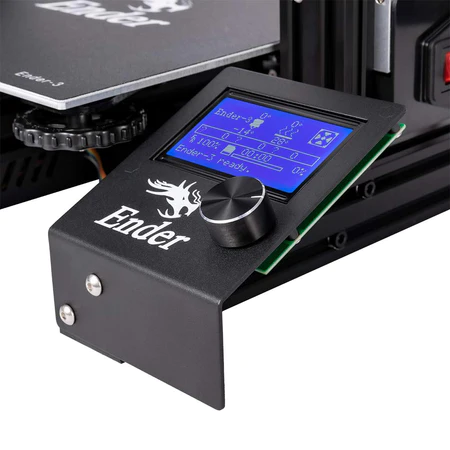

-
Perilla de control de radios de los carros

Enunciado
El siguiente programa lo que hace es...
Hardware
Componentes
| # | Elemento | Cantidad |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Placa de desarrollo ESP32 | 1 |
| 2 | Rotary encoder (37 sensor Kid de Elegoo) | 1 |
Esquemático
A continuación se muestra esquematico del circuito:
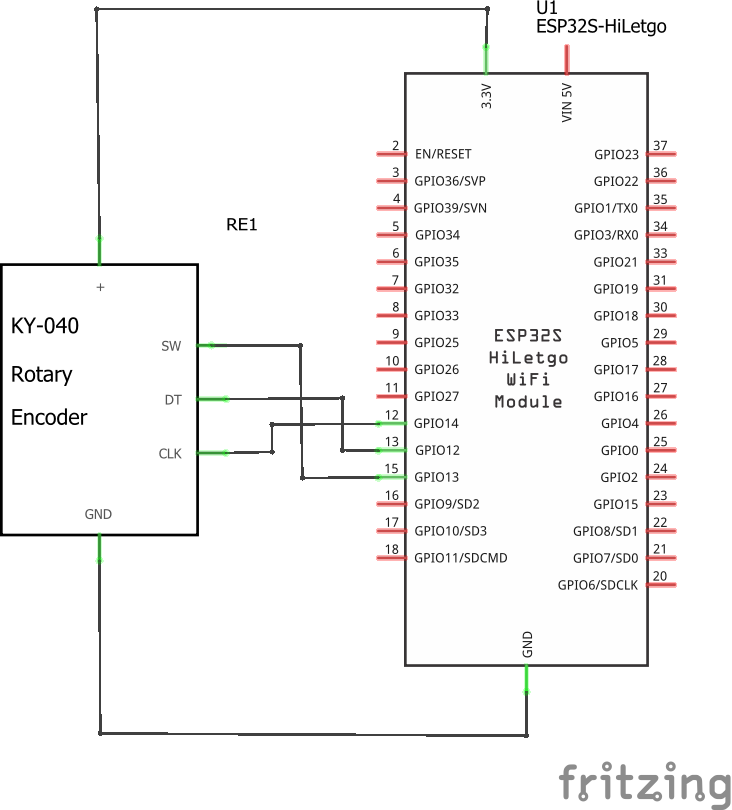
Conexion
A continuación se muestra el diagrama de conexión:
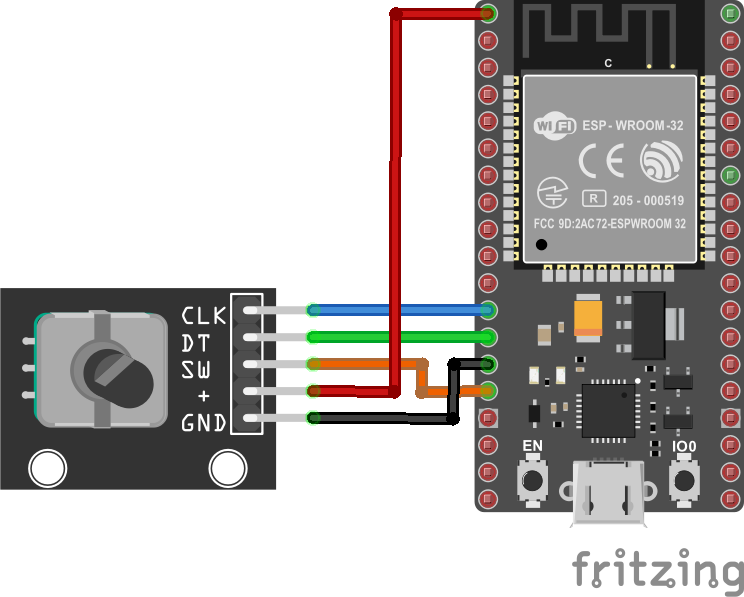
Sofware
La diferentes implementaciones realizadas se muestran a continuación:
- Caso 1 - Implementación por polling
- Caso 2 - Implementación por interrupciones
- Caso 3 - Programa mejorado usando interrupciones
Caso 1 - Implementación por polling
En esta implementación se puede estudiar analizando la simulación online (link)
Código
#include <Arduino.h>
/* ---- Pines I/O ---- */
// Rotary encoder Encoder (I)
#define ENCODER_CLK 14
#define ENCODER_DT 12
#define ENCODER_SW 13
#define DEBUG 1
// Constantes
const char MAX_PUSH_TIME = 50;
// Variables aplicacion
unsigned char counter = 0; // Brillo led integrado
int lastClk = HIGH; // Valor anterior señal CLK
long int resetLastChanged = 0; // cambio reset
/* ---- Inicialización ---- */
void setup() {
// Inicializacion serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// Inicializacion I/O
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN,OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_CLK, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_DT, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_SW, INPUT_PULLUP);
// Impresion en el monitor serial
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
#endif
}
/* ---- Loop infinito ---- */
void loop() {
// Chequeo del reset presionado por un tiempo mayor de MAX_PUSH_TIME
if (digitalRead(ENCODER_SW) == LOW && millis() - resetLastChanged > MAX_PUSH_TIME) {
resetLastChanged = millis();
counter = 0;
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
#endif
analogWrite(LED_BUILTIN,counter);
}
// Actualizancion del brillo
int newClk = digitalRead(ENCODER_CLK);
if (newClk != lastClk) {
// There was a change on the CLK pin
lastClk = newClk;
int dtValue = digitalRead(ENCODER_DT);
if (newClk == LOW && dtValue == HIGH) {
// Aumento brillo
counter++;
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
#endif
}
if (newClk == LOW && dtValue == LOW) {
// Disminución brillo
counter--;
#if DEBUG
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
#endif
}
analogWrite(LED_BUILTIN,counter);
}
}
Test
La salida en el monitor serial de platformio se muestra a continuación:
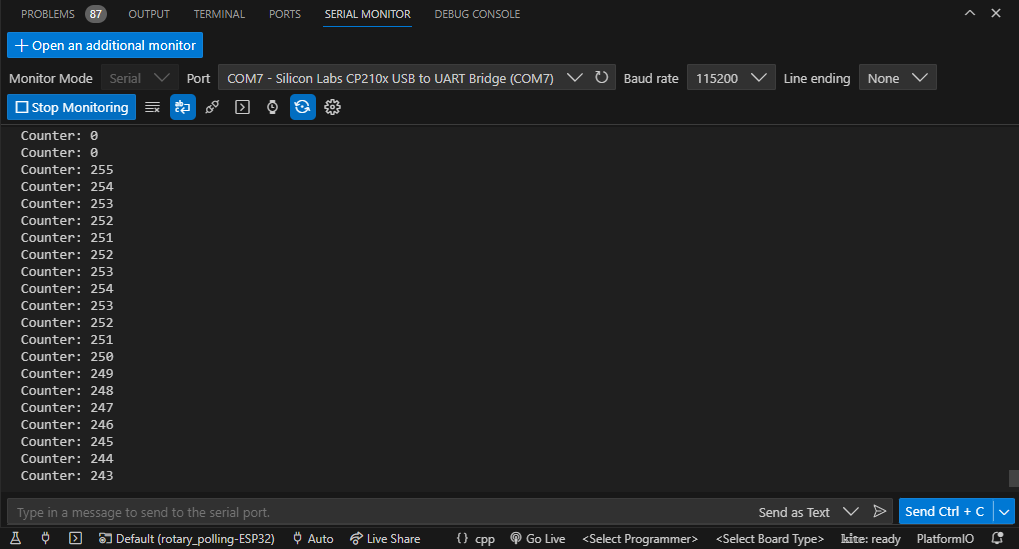
Caso 2 - Implementación por interrupciones
En esta implementación por interrupciones se puede analizar ejecutando la siguiente simulación online (link)
Código
#include <Arduino.h>
/* ---- Pines I/O ---- */
// Rotary encoder Encoder (I)
#define ENCODER_CLK 14
#define ENCODER_DT 12
#define ENCODER_SW 13
#define DEBUG 1
// Constantes
const char DEBOUNCE_TIME = 50;
// Variables aplicacion
volatile unsigned char counter = 0; // Brillo led integrado
int valClk = HIGH;
int dtValue = HIGH;
long int clkLastChanged = 0; // cambio clk
long int resetLastChanged = 0; // cambio reset
// Reset del brillo
void resetEncoder() {
if (digitalRead(ENCODER_SW) == LOW && millis() - resetLastChanged > DEBOUNCE_TIME) {
resetLastChanged = millis();
counter = 0;
}
}
// Actualizancion del brillo
void updateEncoder() {
if ((millis() - clkLastChanged) < DEBOUNCE_TIME) // debounce time is 50ms
return;
dtValue = digitalRead(ENCODER_DT);
if (dtValue == LOW) {
// Serial.println("DOWN");
counter--;
}
else {
// Serial.println("UP");
counter++;
}
clkLastChanged = millis();
}
/* ---- Inicialización ---- */
void setup() {
// Inicializacion serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// Inicializacion I/O
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN,OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_CLK, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_DT, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_SW, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENCODER_CLK), updateEncoder, CHANGE);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENCODER_SW), resetEncoder, CHANGE);
// Impresion en el monitor serial
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
/* ---- Loop infinito ---- */
void loop() {
// Chequeo del reset presionado por un tiempo mayor de MAX_PUSH_TIME
analogWrite(LED_BUILTIN,counter);
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
delay(100);
}
Test
La salida en el monitor serial se muestra a continuación:
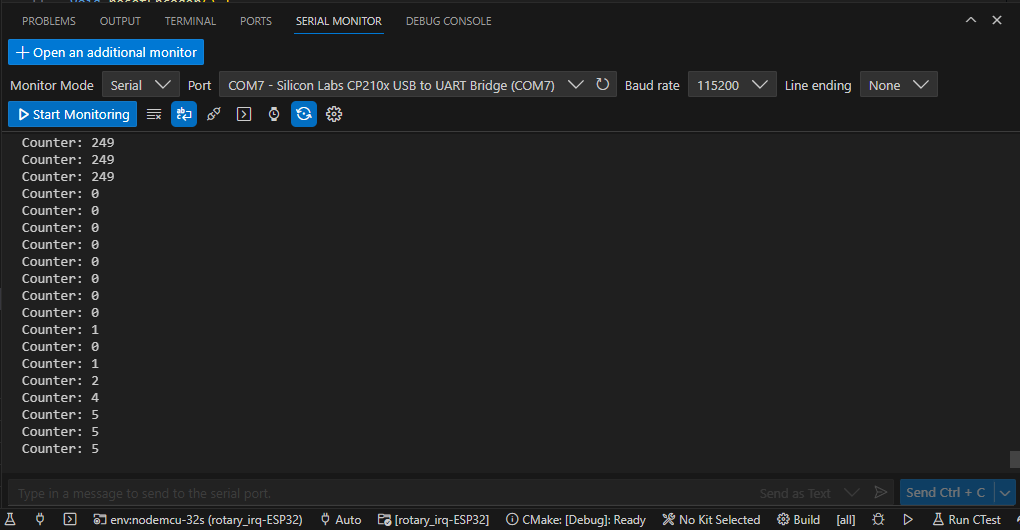
Caso 3 - Programa mejorado usando interrupciones
La implementación de este código se muestra a continuación (Simulación (link))
Código
#include <Arduino.h>
/* ---- Pines I/O ---- */
// Rotary encoder Encoder (I)
#define ENCODER_CLK 14
#define ENCODER_DT 12
#define ENCODER_SW 13
#define DEBUG 1
// Constantes
const char DEBOUNCE_TIME = 50;
// Variables aplicacion
unsigned char counter = 0; // Brillo led integrado
int valClk = HIGH;
int dtValue = HIGH;
long int clkLastChanged = 0; // cambio clk
long int resetLastChanged = 0; // cambio reset
// Reset del brillo
volatile byte SW_EVENT = LOW;
volatile byte CKL_EVENT = LOW;
volatile byte PRINT_EVENT = LOW;
hw_timer_t *timer_100m = NULL; // H/W timer
/* ---- Interrupt handlers ---- */
void ARDUINO_ISR_ATTR event_print(){
PRINT_EVENT = HIGH;
}
void event_sw() {
SW_EVENT = HIGH;
}
void event_clk() {
CKL_EVENT = HIGH;
}
/* ---- Funciones ---- */
// Reset encoder
void resetEncoder() {
if (digitalRead(ENCODER_SW) == LOW && millis() - resetLastChanged > DEBOUNCE_TIME) {
resetLastChanged = millis();
counter = 0;
}
}
// Actualizancion del brillo
void updateEncoder() {
if ((millis() - clkLastChanged) < DEBOUNCE_TIME) // debounce time is 50ms
return;
dtValue = digitalRead(ENCODER_DT);
if (dtValue == LOW) {
// Serial.println("DOWN");
counter--;
}
else {
// Serial.println("UP");
counter++;
}
clkLastChanged = millis();
}
/* ---- Inicialización ---- */
void setup() {
// Inicializacion serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// Inicializacion I/O
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN,OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_CLK, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_DT, INPUT);
pinMode(ENCODER_SW, INPUT_PULLUP);
// Inicializacion de interrupciones externas
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENCODER_CLK), event_clk, CHANGE);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(ENCODER_SW), event_sw, CHANGE);
// Inicializacion del timer
timer_100m = timerBegin(0, 80, true);
timerAttachInterrupt(timer_100m, &event_print, true);
timerAlarmWrite(timer_100m, 100000, true);
timerAlarmEnable(timer_100m);
// Impresion en el monitor serial
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
}
/* ---- Loop infinito ---- */
void loop() {
// Evento reset
if (SW_EVENT == HIGH) {
// Serial.println("Debug: Reset event");
resetEncoder();
analogWrite(LED_BUILTIN,counter);
SW_EVENT = LOW; // No olvidar (atencion del evento)
}
// Evento de actualización del contador
if (CKL_EVENT == HIGH) {
// Serial.println("Debug: Update event");
updateEncoder();
analogWrite(LED_BUILTIN,counter);
CKL_EVENT = LOW; // No olvidar (atencion del evento)
}
// Evento para la impresion en pantalla
if (PRINT_EVENT == HIGH) {
Serial.print("Counter: ");
Serial.println(counter);
PRINT_EVENT = LOW; // No olvidar (atencion del evento)
}
}
Test
Queda pendiente capturar la salida...
Referencias
- https://www.upesy.com/blogs/tutorials/rotary-encoder-esp32-with-arduino-code
- https://circuitdigest.com/microcontroller-projects/esp32-timers-and-timer-interrupts
- https://www.electronicwings.com/esp32/esp32-timer-interrupts
- https://deepbluembedded.com/esp32-timers-timer-interrupt-tutorial-arduino-ide/
- https://esp32io.com/tutorials/esp32-rotary-encoder
- https://github.com/igorantolic/ai-esp32-rotary-encoder
- https://www.upesy.com/blogs/tutorials/rotary-encoder-esp32-with-arduino-code
- https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/libraries/ai-esp32-rotary-encoder/
- https://electricdiylab.com/how-to-connect-optical-encoder-with-esp32/
- https://esp32tutorials.com/esp32-pulse-counter-pcnt-esp-idf-rotary-encoder/
- https://www.adafruit.com/product/5734